
Product Design Services vs. Industrial Design Services
July 29, 2021
Design is an essential part of manufacturing new products, with product design and industrial design being an important part of the process. While product design and industrial design can work in similar fields, there are some differences between the two. The focus of their work and their key services are what differentiates these two commonly associated design types.
In general, product designers focus on making a product more appealing to a niche audience, while industrial designers focus on making a product ready for large-scale manufacturing. Industrial designers ask themselves how a product can be changed or updated during the process of production to make it ready to sell to the general public. Product designers will ask themselves what features can be changed, enhanced, or revised to appeal to their target audience and increase product sales.
Industrial Design
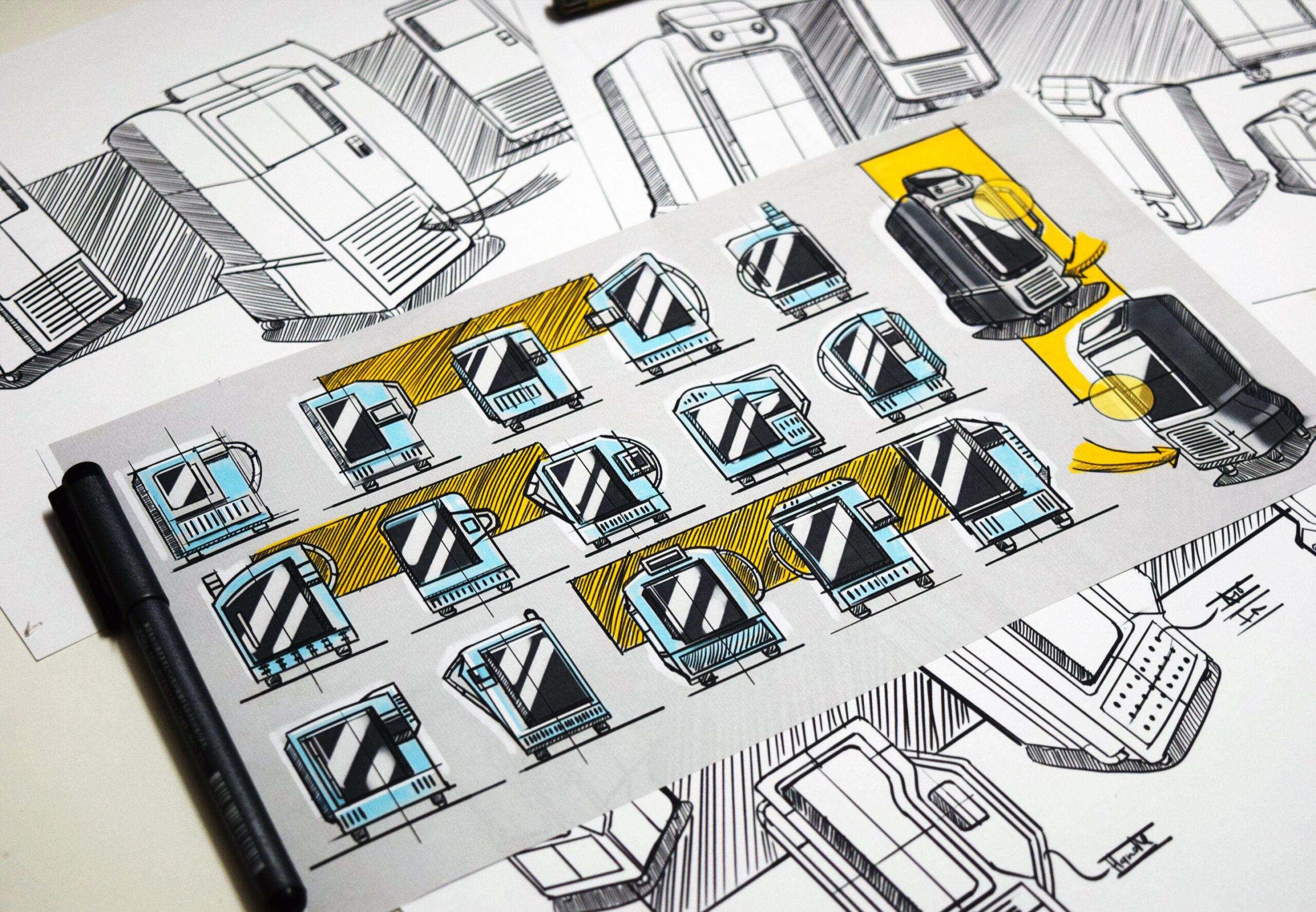
According to the Industrial Designers Society of America (IDSA), industrial designers pay attention to appearance, functionality, and manufacturability throughout the design process. The design process is usually composed of two phases: the ideation or concept phase and the final phase. In the ideation or concept phase, industrial designers use mediums such as 3D models and sketches to test possible products and create prototypes. The final phase consists of production, fulfillment, and marketing. As industrial designers research and test their ideas, they must understand the needs and wants of the average customer. This requires them to be knowledgeable about current trends, since their goal is to create a product that sells to as many people as possible. Two examples of products that industrial designers work on are cars and cell phones. In the case of cars, they determine how to make a car most suitable for mass production and consumption.
Product Design
In contrast, product designers can cater to a more niche audience. In their article “Five Often-Overlooked Elements of Product Design for Faster Success,” Forbes notes that product designers aim to make their product the answer to their customers’ problems. Product designers also prototype and test their products, but they do this with their target audience in mind. Forces describes this as, “delivering the right features, with the right user experience, to the right people.” Two examples of product design are cereal boxes and soap bottles. Using soap bottles as an example, product designers manufacture the product so that it answers their customers’ specific needs, such as more eco-friendly packaging.
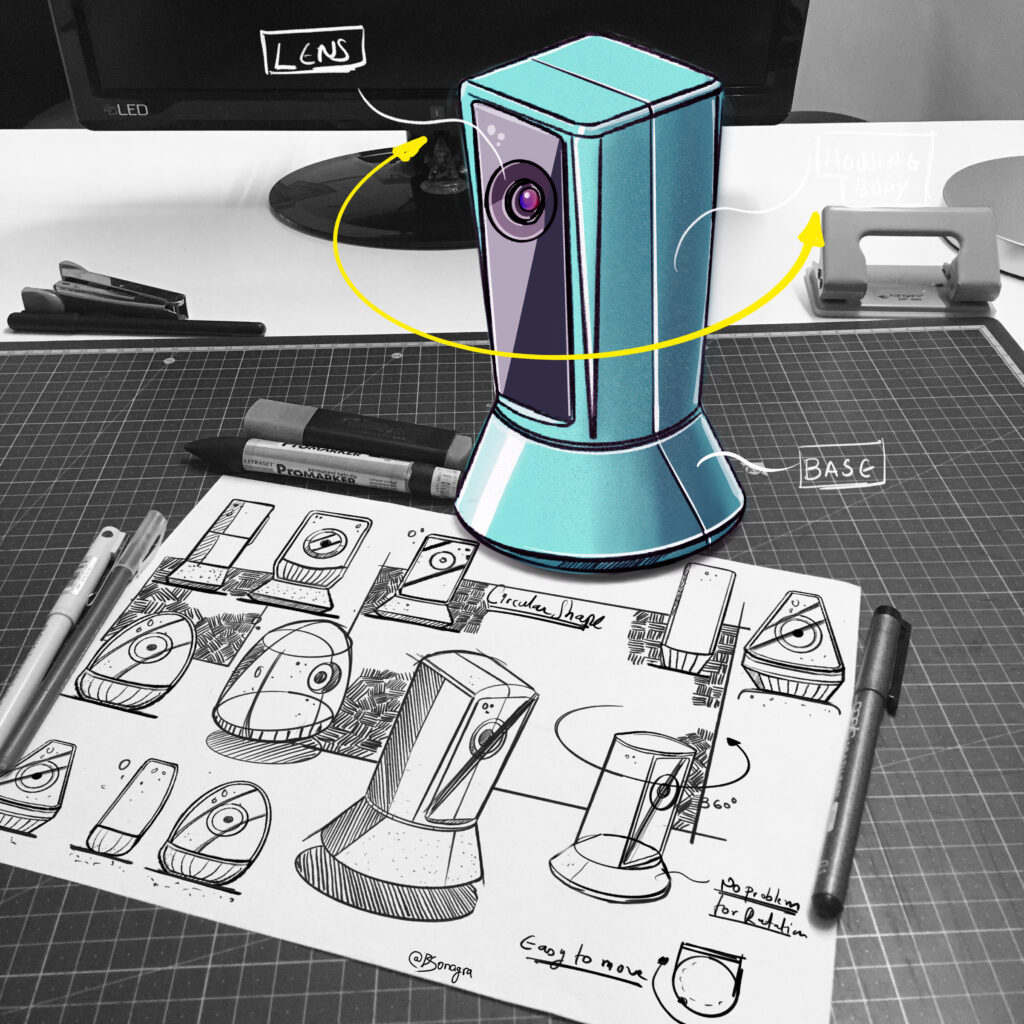
Conclusion
Overall, product and industrial design use similar creative processes, but have different goals. Industrial design manufactures products for mass production, while product design centers on appealing to and increasing sales within a target audience.
